The Hidden Link Between Oral Bacteria and Stroke Risk: Insights for Dental Professionals
.
Emerging research has unveiled a compelling connection between specific oral bacteria and an increased risk of stroke. A study presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2025 highlights the role of Streptococcus anginosus, a common bacterium in the mouth and gut, in elevating stroke risk. This discovery underscores the critical importance of oral health in preventing systemic diseases, offering valuable insights for dental practitioners.
Key Findings: The Role of Streptococcus anginosus in Stroke
Researchers from the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Osaka, Japan, conducted a study comparing the oral and gut microbiota of recent stroke survivors to individuals without a history of stroke. Their analysis revealed significant differences in bacterial composition:
- Elevated Levels of Streptococcus anginosus: This bacterium was found in higher abundance in both the saliva and gut of stroke patients compared to the control group.
- Increased Stroke Risk: The presence of Streptococcus anginosus in the gut was independently associated with a 20% higher likelihood of stroke, even after adjusting for traditional vascular risk factors.
- Poor Prognosis: Stroke survivors with elevated Streptococcus anginosus levels faced a higher risk of death and major cardiovascular events over a two-year follow-up period.
Conversely, certain beneficial gut bacteria were linked to a reduced stroke risk:
- Anaerostipes hadrus: Associated with an 18% decrease in stroke risk.
- Bacteroides plebeius: Linked to a 14% reduction in stroke risk.
Understanding the Mechanism: How Oral Bacteria Influence Stroke Risk
The study suggests that Streptococcus anginosus contributes to tooth decay by producing acids that erode tooth enamel. Beyond dental implications, the presence of this bacterium in the gut may lead to systemic inflammation, a known risk factor for stroke. This highlights the intricate relationship between oral health and overall cardiovascular well-being.
Implications for Dental Practice: Preventive Strategies
For dental professionals, these findings emphasize the importance of comprehensive oral care in mitigating stroke risk. Key recommendations include:
- Promote Optimal Oral Hygiene: Encourage patients to maintain regular brushing and flossing routines to minimize the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
- Advocate for Reduced Sugar Intake: Educate patients on the role of sugar in fostering bacterial growth that leads to tooth decay and potential systemic issues.
- Utilize Targeted Toothpaste: Recommend toothpaste formulations that specifically combat bacteria like Streptococcus anginosus to enhance preventive care.
- Monitor Oral Health Vigilantly: Regular dental check-ups can help identify and address bacterial imbalances before they contribute to systemic health problems.
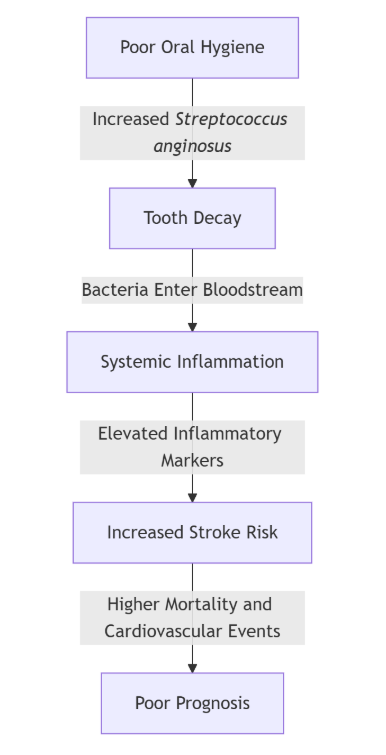
Visualizing the Connection: Oral Bacteria and Stroke Risk
To illustrate the relationship between oral bacteria and stroke risk, consider the following flowchart:
This diagram demonstrates how inadequate oral hygiene can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, resulting in systemic inflammation and heightened stroke risk.
Conclusion: Integrating Oral and Systemic Health
This research reinforces the critical role dental professionals play in safeguarding not only oral health but also overall systemic well-being. By implementing targeted preventive strategies and educating patients on the broader health implications of oral care, dental practitioners can contribute significantly to reducing stroke risk and promoting long-term health.
Sources
ScienceDaily – A common mouth and gut bacteria may be linked with increased stroke risk – January 30, 2025