Diabetes increases risk of tooth decay – new research finds
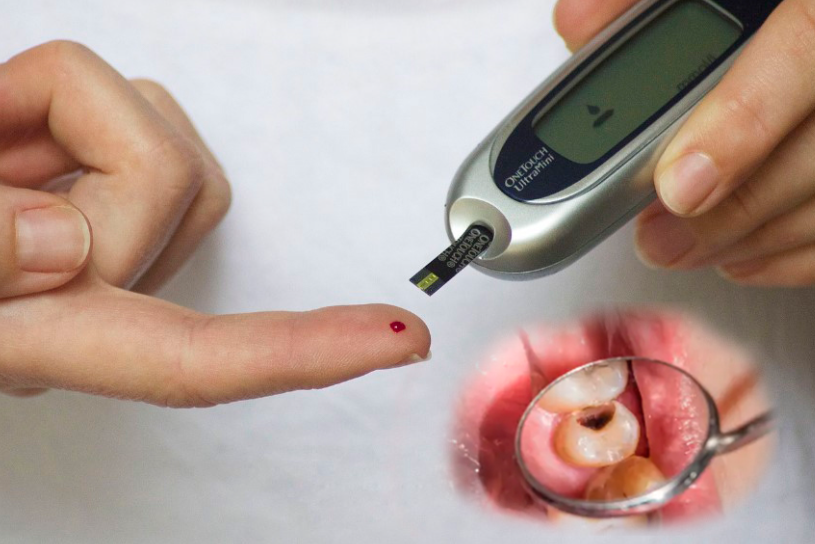
In recent years, there has been growing concern about the impact of diabetes on dental health. Individuals with both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are found to be more susceptible to tooth decay, leading to higher rates of cavities and tooth loss. A groundbreaking study conducted by researchers at Rutgers sheds light on the underlying reasons behind this phenomenon and the implications it has for dental health. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the findings of this study and explore the critical connection between diabetes and dental deterioration.
The Diabetes Epidemic: A Growing Concern
Diabetes has reached epidemic proportions, with millions of individuals affected worldwide. It is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, and it can have far-reaching consequences on various aspects of health. While the association between diabetes and cardiovascular problems is well-documented, the impact on oral health is an area that has garnered increasing attention in recent years.
Unraveling the Mystery: Diabetes and Dental Health
The Rutgers study, led by Mohammad Ali Saghiri, an assistant professor of restorative dentistry, sought to uncover the mechanisms by which diabetes influences dental health. The researchers induced Type 1 diabetes in 35 mice and compared their dental health with that of 35 healthy controls over a span of 28 weeks.
The Role of Enamel and Dentin
To understand the link between diabetes and tooth decay, it is essential to appreciate the significance of enamel and dentin. Enamel is the hard, outer layer of teeth, while dentin is the tough tissue beneath it that provides structural support to our teeth.
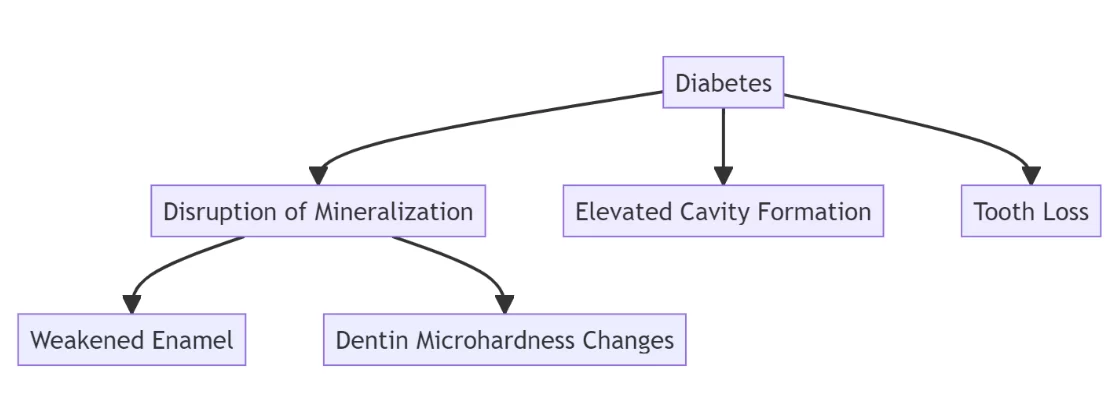
The study revealed a startling revelation: although the diabetic mice and the healthy controls started with comparable dental conditions, significant changes occurred over the study period. After just 12 weeks, the enamel in the diabetic mice began to exhibit a marked softening, and this trend continued to worsen as the study progressed. Moreover, noticeable differences in the microhardness of dentin became evident by the 28th week.
The Implications for Dental Health
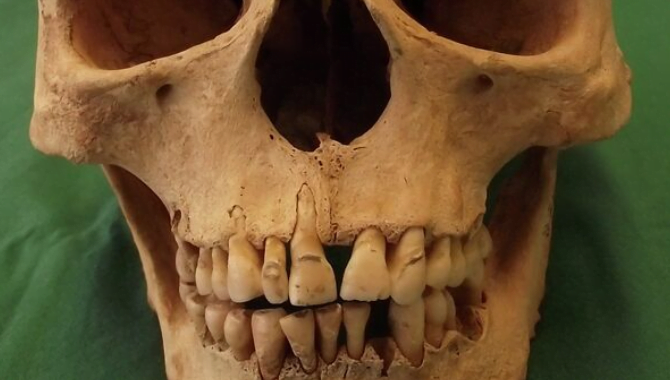
These findings shed crucial light on the heightened susceptibility of individuals with diabetes to dental issues. It’s long been observed that such individuals experience elevated rates of cavity formation and tooth loss, with conventional dental treatments like fillings proving less effective and durable. However, the exact reasons behind these phenomena were not fully understood until now.
Diabetes and Mineralization: A Disrupted Process
One key insight from the study is how diabetes interferes with the natural process of adding minerals to teeth as they wear down through normal usage. This process, known as mineralization, is essential for maintaining the strength and integrity of teeth. Diabetes disrupts this process, leaving teeth more vulnerable to decay and damage.
The Need for Further Research
Dr. Saghiri emphasizes the pressing need for more extensive research in this area. As the global diabetes population continues to grow at an alarming rate, there is a substantial demand for treatments that can help individuals with diabetes maintain their dental health. Historically, dental health has not been a major focus of diabetes-related research, but this study underscores its importance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study conducted by Rutgers researchers provides valuable insights into the relationship between diabetes and tooth decay. The softening of enamel and changes in dentin microhardness observed in diabetic individuals help explain the higher rates of dental issues within this population. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for developing effective treatments that can mitigate the impact of diabetes on dental health.
As researchers continue to delve into this complex relationship, the hope is that innovative solutions will emerge to help individuals with diabetes maintain healthy smiles and lead fulfilling lives, free from the burden of dental complications.
Sources
- Science Day – Diabetes may weaken teeth and promote tooth decay – May 31, 2022
- ScienceDirect – Diabetes negatively affects tooth enamel and dentine microhardness: An in-vivo study – July 2022