How to Select the Perfect Abutment for Your Dental Implant: A Comprehensive Guide

In the world of dentistry, dental implants have emerged as a game-changer, providing a highly effective and long-lasting solution for individuals with missing teeth. At the heart of this cutting-edge technology lies the abutment - a crucial component connecting the dental implant to the final restoration. With so many options on the market, selecting the right abutment for a successful implant can be a daunting task, even for seasoned dental professionals. But fear not, because we're here to guide you through the process and simplify your decision-making.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the essential factors to consider when choosing the perfect abutment for your implant. We’ll discuss the different types of abutments available, and examine the importance of material choice, as well as the impact of patient-specific factors such as bone quality, implant position, and esthetic requirements. So let’s start with a burning question: how can you ensure that the abutment you select will not only provide a solid foundation for your patient’s new tooth but also deliver the best possible esthetic and functional outcome? Read on to uncover the answer and unlock the secrets to successful abutment selection!
Understanding the Role of Abutments in Implant
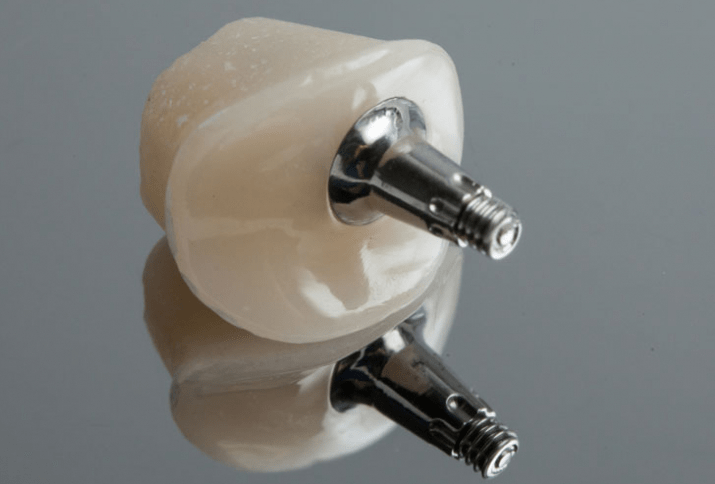
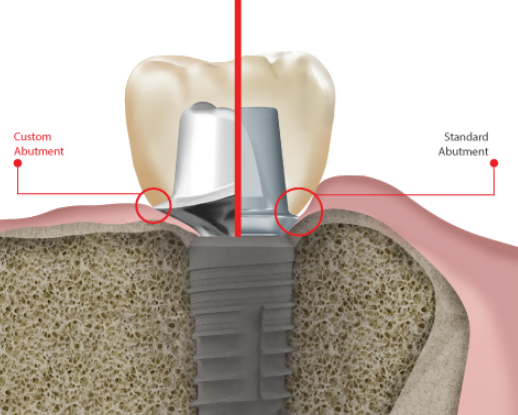
Selecting an abutment for a dental implant refers to the process of choosing the appropriate connecting component that links the dental implant (which is anchored in the jawbone) to the final restoration or prosthesis, such as a crown, bridge, or denture. The abutment plays a crucial role in the success of the dental implant, as it ensures proper support, stability, and esthetics for the final restoration.
There are various factors to consider when selecting the right abutment for a dental implant, including the type of abutment, material used, implant position, patient-specific factors (e.g., bone quality, gum thickness), and esthetic requirements. These factors all contribute to the long-term success and appearance of the dental implant, ultimately resulting in a more natural-looking and comfortable solution for patients with missing teeth.
The Importance of Proper Abutment Selection for Implant
Selecting the appropriate abutment for a dental implant is essential for several reasons:
- Proper fit and support: The abutment connects the dental implant to the final restoration, ensuring a secure and stable fit. Choosing the right abutment helps to achieve proper support for the prosthetic tooth, which is critical for long-term success and patient comfort.
- Esthetics: The right abutment can significantly affect the overall appearance of the final restoration. Abutments come in different materials, such as titanium, zirconia, or hybrid (titanium base with zirconia on top), which can influence the final esthetic outcome. Selecting the best abutment for the patient’s specific situation can help achieve a more natural and pleasing appearance.
- Functionality: The correct abutment selection is crucial for proper functionality of the implant and restoration. It ensures that the forces exerted on the implant during biting and chewing are evenly distributed, reducing the risk of complications or implant failure.
- Individualized treatment: Each patient’s clinical situation is unique, and selecting the right abutment allows dental professionals to tailor the treatment to the specific needs and circumstances of the patient, such as bone quality, gum thickness, and implant position.
- Longevity: A well-chosen abutment can contribute to the overall longevity of the dental implant and the final restoration. A proper fit and appropriate materials can help reduce the risk of complications, such as peri-implantitis, which could lead to implant failure and the need for additional treatment.
Selecting the right abutment for a dental implant is a critical step in the treatment process. It ensures proper fit, support, esthetics, functionality, and longevity of the implant and restoration, ultimately leading to a successful outcome and increased patient satisfaction.
Expert Insights: Tips and Recommendations for Selecting the Right Abutment for Your Dental Implant
I am thrilled to share my thoughts on selecting the perfect abutment for dental implants! Trust me, it’s one of the most crucial aspects of the entire implant process, and getting it right can make a world of difference for our patients.
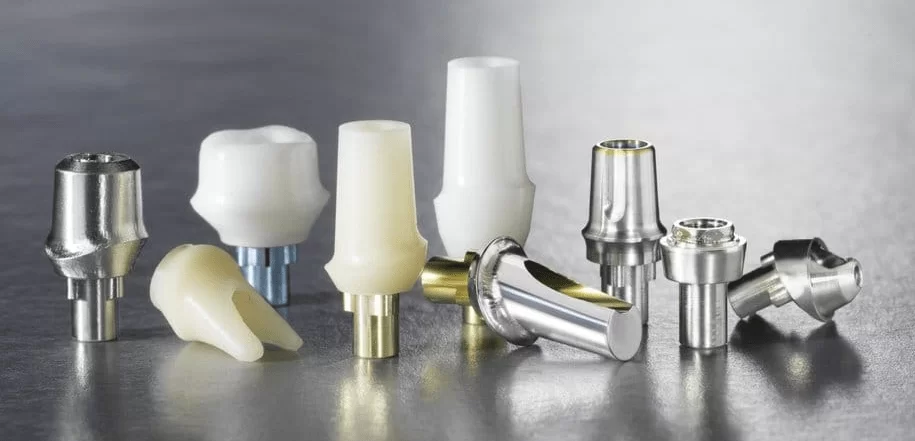
First, let’s talk about materials. Titanium abutments have been the gold standard for years, and I must say, they’re incredibly reliable and durable. But then, along came zirconia abutments, which are not only strong but also offer fantastic esthetic results, especially for those with thin or translucent gums. And let’s not forget the hybrid abutments – they combine the best of both worlds, with the strength of titanium and the esthetics of zirconia. It’s like a match made in dental heaven!
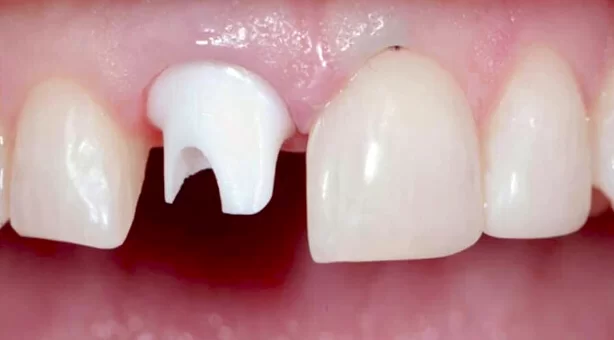
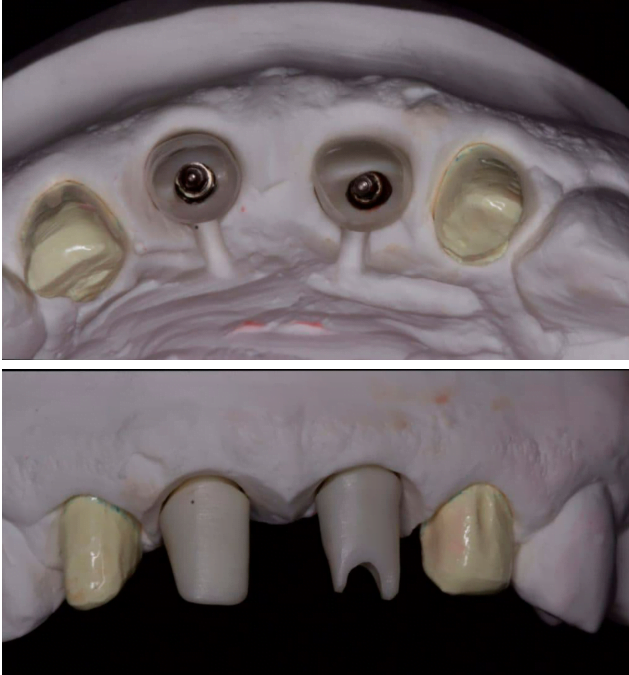
Now, when it comes to selecting the right type of abutment, I’m always impressed by the sheer variety of options out there. We’ve got prefabricated abutments, which are quick and cost-effective, but then there are custom abutments that can be tailored to the patient’s specific needs. Custom abutments are fantastic for achieving that perfect, natural-looking smile. It’s like a bespoke suit, but for your teeth!
Of course, we can’t overlook the importance of patient-specific factors, like bone quality, gum thickness, and implant position. These elements play a significant role in determining the best abutment choice for each individual case. I’m always excited to see how these factors come together to create a beautifully functional and esthetic result.
Selecting the right abutment for a dental implant is like solving an intricate puzzle – one that requires skill, knowledge, and a keen eye for detail. But when all the pieces come together, the result is simply amazing: a sturdy, natural-looking restoration that can truly transform a patient’s smile and quality of life. It’s incredibly rewarding to see the positive impact these implant procedures can have on our patients’ self-esteem and overall oral health.
So, when it comes to selecting abutments for dental implants, there’s a lot to consider and a lot to be excited about. I can’t wait to see what the future holds for this field and how it will further enhance our ability to create stunning, long-lasting, and life-changing dental implant restorations!
Comparing Abutment Types, Materials, Sizes, and Shapes
When selecting an abutment for a dental implant, it is essential to consider various factors to make an informed decision. Here is a comparison table that elaborates on each ingredient involved in the selection process:
| Factor | Prefabricated Abutment | Custom Abutment | Hybrid Abutment |
| Material | Titanium, Zirconia | Titanium, Zirconia | Titanium base with Zirconia top |
| Esthetics | Good esthetics with titanium; better esthetics with zirconia | Superior esthetics due to customization | Excellent esthetics due to zirconia top |
| Strength and durability | High strength and durability with titanium; less strength with zirconia | High strength and durability with titanium; less strength with zirconia | Excellent strength due to titanium base |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to customization | Moderate to high cost |
| Suitability for thin gums | Less suitable with titanium; more suitable with zirconia | Highly suitable due to customization | Highly suitable due to zirconia top |
| Ease of modification | Limited modification possibilities | Unlimited modification possibilities | Limited modification possibilities |
| Implant position compatibility | Compatible with most implant positions | Ideal for complex implant positions | Compatible with most implant positions |
When selecting an abutment for a dental implant, consider the following factors:
- Material: Choose between titanium, zirconia, or hybrid abutments based on durability, esthetics, and patient-specific factors.
- Esthetics: Consider the patient’s gum thickness and the location of the implant when selecting an abutment for optimal esthetic results.
- Strength and durability: Titanium abutments offer high strength and durability, while zirconia abutments may be less strong but provide better esthetics. Hybrid abutments combine the benefits of both materials.
- Cost: Prefabricated abutments are generally more cost-effective, while custom abutments and hybrid abutments may come at a higher price point.
- Suitability for thin gums: Zirconia and hybrid abutments are more suitable for patients with thin or translucent gums, while titanium abutments may be less suitable in these cases.
- Ease of modification: Custom abutments offer unlimited modification possibilities, while prefabricated and hybrid abutments have limited modification options.
- Implant position compatibility: Custom abutments are ideal for complex implant positions, while prefabricated and hybrid abutments are compatible with most implant positions.
Selecting the appropriate abutment for a dental implant involves evaluating each of these factors based on the patient’s unique needs and clinical situation. By comparing the different types of abutments and considering the factors mentioned above, dental professionals can make the best decision for their patients, ensuring a successful implant restoration with optimal esthetic and functional outcomes.
Essential Equipment for Abutment Selection and Placement in Implant
Here is a table listing the equipment and tools that dental professionals may need when working with dental implants and selecting the appropriate abutment:
| Equipment/Tool | Purpose/Function |
| Dental Implant Kit | Contains various instruments for implant placement, such as drills, drivers, etc. |
| Surgical Handpiece | Used to drill the osteotomy and prepare the site for implant placement |
| Implant Motor | Provides controlled speed and torque for the surgical handpiece during drilling |
| Surgical Guide | Aids in accurate implant placement and proper angulation |
| Periodontal Probe | Measures gingival and bone levels to assess soft tissue health |
| Dental Caliper | Measures the width and height of teeth to determine abutment size and shape |
| Digital Caliper | Provides precise measurements of implant components and abutments |
| Dental Mirror | Allows visualization of hard-to-see areas during implant placement and abutment selection |
| Explorer/Probe | Detects and evaluates implant margins and seating of the abutment |
| Tweezers/Forceps | Used for handling and positioning abutments and other small components |
| Torque Wrench | Applies the required torque for securing the abutment to the implant |
| Impression Tray | Used to take an accurate impression jaws |
A Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing and Placing the Right Abutment for Your Dental Implant
Step 1: Evaluate the clinical situation
- Review the patient’s dental and medical history.
- Perform a comprehensive clinical examination, including periodontal assessment, occlusal analysis, and radiographic evaluation (e.g., CBCT or panoramic radiographs).
- Determine the implant position, bone quality, and gum thickness.
Step 2: Choose the appropriate abutment type
- Decide between prefabricated, custom, or hybrid abutments based on the patient’s clinical situation, esthetic requirements, and implant position.
- Consider using a custom abutment for complex implant positions or when superior esthetics are required.
- Prefabricated abutments may be suitable for most cases and can be more cost-effective.
Step 3: Select the abutment material
- Choose between titanium, zirconia, or hybrid abutments based on the patient’s specific needs, esthetic requirements, and gum thickness.
- Titanium abutments offer high strength and durability.
- Zirconia abutments provide better esthetics, especially in cases with thin or translucent gums.
- Hybrid abutments combine the strength of titanium with the esthetics of zirconia.
Step 4: Determine the appropriate abutment size and shape
- Use dental calipers or digital calipers to measure the width and height of the adjacent teeth.
- Select an abutment that closely resembles the size and shape of the natural tooth, ensuring proper support for the final restoration and esthetically pleasing results.
- Keep in mind the occlusal scheme and adjacent teeth contacts when selecting the abutment shape.
Step 5: Assess the emergence profile
- Evaluate the abutment’s emergence profile to ensure it gradually widens from the implant platform to the restoration, mimicking the contours of the natural tooth and supporting the surrounding soft tissues.
- Select an abutment with an appropriate emergence profile to promote healthy gingival tissue and minimize plaque accumulation.
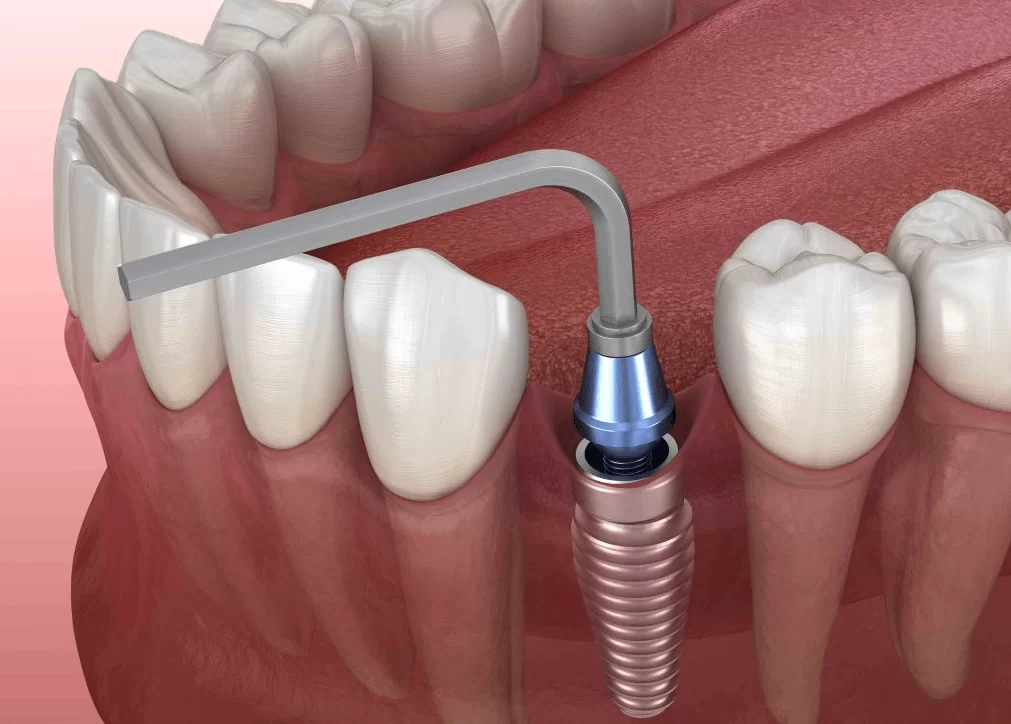
Step 6: Verify proper fit and seating
- Place the selected abutment onto the implant and check its fit using an explorer or probe.
- Ensure that the abutment is seated correctly, with no gaps or rocking movements, to prevent complications such as peri-implantitis and implant failure.
- Check the occlusion and interproximal contacts to ensure proper function and stability.
Step 7: Secure the abutment
- Use a torque wrench to apply the manufacturer-recommended torque for securing the abutment to the implant.
- Confirm the stability of the abutment-implant connection and adjust if necessary.
Step 8: Take the final impression
- After the abutment is securely attached to the implant, take an accurate impression using an impression tray and appropriate impression material.
- Send the impression to the dental laboratory for the fabrication of the final restoration (e.g., crown, bridge, or denture).
Step 9: Communicate with the dental laboratory
- Provide the dental laboratory with detailed information about the selected abutment, material, size, shape, and emergence profile.
- Discuss the patient’s esthetic and functional requirements, as well as any specific instructions for the final restoration.
Step 10: Evaluate the final restoration
- Once the dental laboratory completes the final restoration, evaluate its fit, occlusion, and esthetics on the selected abutment.
- Make any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal function, comfort, and appearance.
Step 11: Deliver the final restoration
- Cement or screw the final restoration onto the abutment, following the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations.
- Check the occlusion, interproximal contacts, and overall esthetics to ensure patient satisfaction.
Step 12: Schedule follow-up appointments
- Schedule regular follow-up appointments with the patient to monitor the health of the implant, abutment, and final restoration.
- Perform routine dental cleanings, radiographs, and examinations to ensure the long-term success of the dental implant and to address any potential complications early on.
By following these step-by-step instructions, dental professionals can effectively select the appropriate abutment for a dental implant, ensuring a successful outcome with optimal esthetic and functional results.
Frequently Asked Questions about Abutment Selection for Implant
Q1: What is an abutment and why is it important?
A1: An abutment is a connecting component that links a dental implant to the final restoration, such as a crown, bridge, or denture. Selecting the right abutment is essential for proper support, stability, and esthetics of the final restoration, contributing to the long-term success of the dental implant.
Q2: What are the different types of abutments?
A2: There are three main types of abutments: prefabricated, custom, and hybrid. Prefabricated abutments are ready-made and available in various sizes and shapes. Custom abutments are designed specifically for the patient’s unique clinical situation. Hybrid abutments have a titanium base with a zirconia top, combining the strength of titanium and the esthetics of zirconia.
Q3: How do I choose the right abutment material?
A3: The choice between titanium, zirconia, or hybrid abutments depends on factors such as esthetic requirements, patient-specific factors (e.g., gum thickness), and implant position. Titanium abutments are strong and durable, while zirconia abutments offer better esthetics. Hybrid abutments provide both strength and esthetics.
Q4: How does the implant position affect abutment selection?
A4: Implant position can influence the choice of abutment type and material. For complex implant positions or when optimal esthetics are required, custom abutments may be more suitable. Prefabricated and hybrid abutments are generally compatible with most implant positions, but may be less suitable for challenging or highly esthetic cases.
Q5: What factors should be considered when selecting the abutment size and shape?
A5: When choosing the abutment size and shape, consider the dimensions of the adjacent teeth, occlusal scheme, and interproximal contacts. The selected abutment should closely resemble the size and shape of the natural tooth to ensure proper support for the final restoration and esthetically pleasing results.
Q6: How do I ensure a proper fit and seating of the abutment?
A6: To verify the proper fit and seating of the abutment, place it onto the implant and check for gaps or rocking movements using an explorer or probe. Ensure that the abutment is seated correctly and securely to prevent complications such as peri-implantitis and implant failure.
Q7: Can abutments be modified or adjusted?
A7: Custom abutments offer unlimited modification possibilities, while prefabricated and hybrid abutments have limited modification options. If necessary, abutments can be adjusted by a dental laboratory or, in some cases, by the dental professional during the clinical procedure to achieve an optimal fit, esthetics, and function.
Q8: How often should the abutment and implant be checked after the final restoration is placed?
A8: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the health of the implant, abutment, and final restoration. Schedule routine dental cleanings, radiographs, and examinations to ensure the long-term success of the dental implant and to address any potential complications early on.
Q9: Can abutments be replaced or changed after they have been placed?
A9: Yes, abutments can be replaced or changed if necessary, such as when there are issues with fit, esthetics, or function. However, it is essential to consult with a dental professional to determine the best course of action for the specific clinical situation.
Q10: What role do dental laboratories play in abutment selection and fabrication of the final restoration?
A10: Dental laboratories play a crucial role in the fabrication of custom abutments and the final restoration. Dental professionals need to provide detailed information about the selected abutment, material, size, shape, and emergence profile, as well as any specific instructions for the final restoration. Close collaboration between the dental professional and the laboratory ensures the best possible outcome for the patient.