Biodegradable implants in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery
Biodegradable implants are not a new technology, but in recent years have become more widespread in the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery and dentistry. They are essentially medical devices with different shapes and properties that gradually resorb in the body. They are made of biocompatible materials that do not cause allergic reactions or rejection. The first studies on the use of bioabsorbable polymers in animals were conducted in the late 60s and early 70s of the last century, but only recently new materials and sufficient knowledge about the processes that occur in the body to widely apply biodegradable implants in medicine for a wide range of clinical cases.
The main types of biodegradable implants are as follows
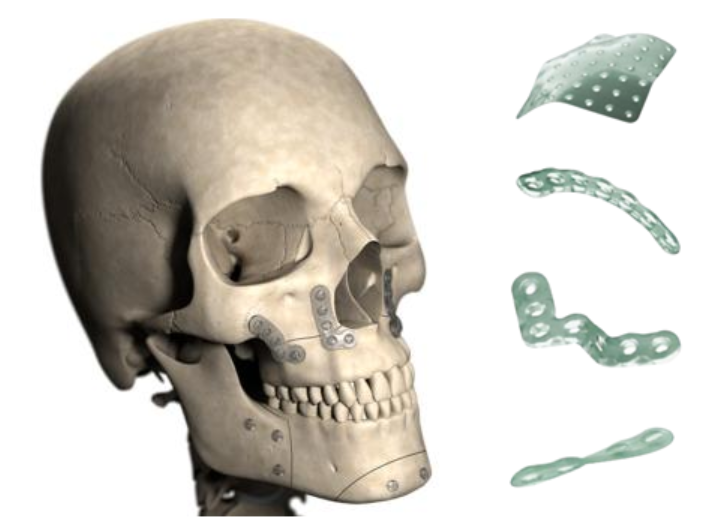
- Biodegradable plates – there are flat and concave varieties. Typical size is 20×100 or 20×65 mm. The thickness depends on the application and can be 1 mm; 1.3 mm; 1.4 mm; 1.7 mm. The entire surface of the plate is perforated for fixing the plate with a screw to the bone tissue. In addition to universal plates, which are equally well suited for different parts of the skeleton, there are specialized plates of a certain shape, for example, for craniofacial surgery or treatment of ankle fractures. In order to shape the biodegradable plate, it is necessary to heat it in a water bath.
.
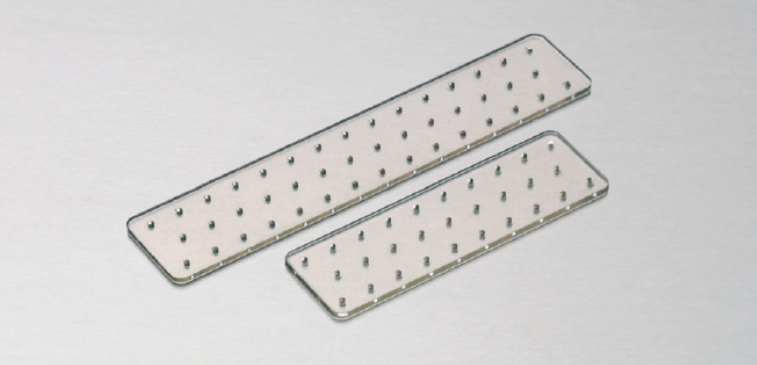
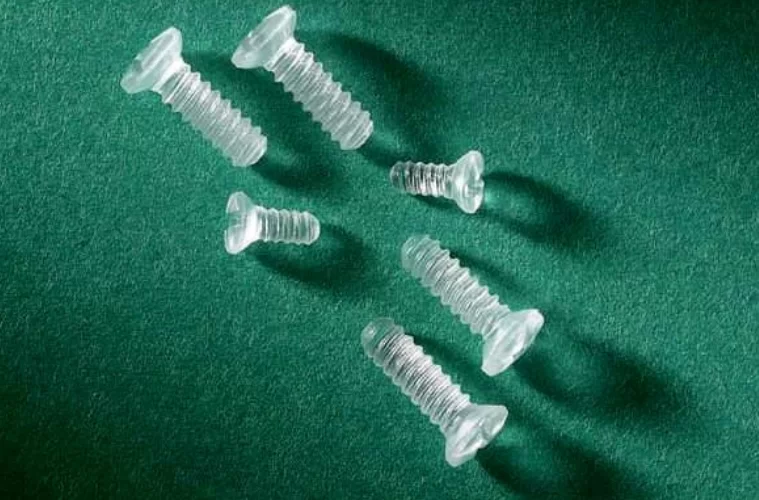
. - Biodegradable screws are used to fix the plates to the bone tissue and are also fully recycled by the body over time. The screws may have different mechanical properties and resorption rates, but most often they are composed of the same substances but in different proportions.
.

. - Biodegradable pins are also used for fixation of meshes, membranes, less frequently plates to bone. The diameter of the pins is usually smaller compared to screws from 1.5 to 3.2 mm, length from 20 to 70 mm.
.
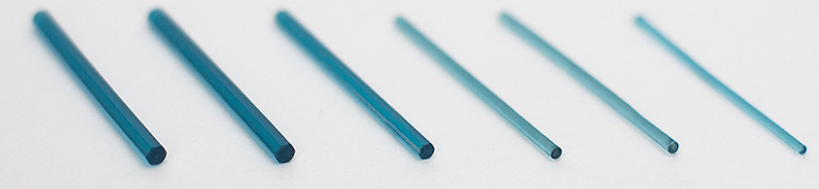
. - Biodegradable meshes. The key difference between meshes and perforated plates is the thickness. For nets it is 0.6-0.7 mm, while the thickness of plates starts from 1.4 mm. The nets are produced in standard sizes, the most common of which are 45×45 mm or 90×90 mm. If necessary, you can cut out a fragment of the desired shape with scissors. The nets also have holes for pre-installation of screws.
.
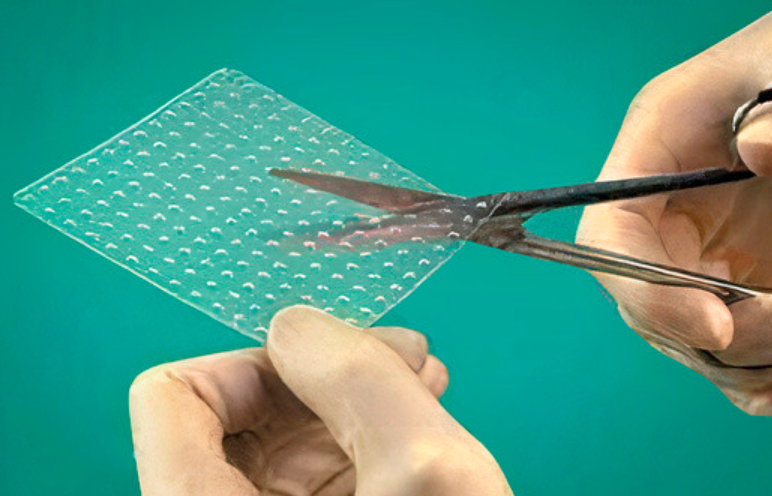
. - Biodegradable membranes do not have holes are available in the form of plates of standard size 30×40 mm. They are designed specifically for dental applications and serve as a barrier membrane for directed bone regeneration. Several templates are included in the kit, according to which the membrane can be cut to the required shape and size. The membrane structure is three-layered and it does not matter which side of the bone the membrane is placed on. The membranes consist of L-lactic acid, D-lactic acid, glycolic acid and trimethylene carbonate. They provide a barrier for 8-12 weeks and then resorb. Biodegradable membranes are stiffer and stronger compared to collagen membranes and do not need repeated surgery to extract them unlike Teflon membranes.
The difference between different types of multi units that you can use and different types of screw
. - The bone graft substitute is made of biologically active glass, which when in contact with natural biological fluids (blood, bone marrow, and even sterile saline and water) forms a layer of silicon dioxide gel and calcium phosphate, which create the basis for bone formation. The bone graft substitute is gradually replaced by new bone tissue. The healing process can take up to 6 months. The field of application of this material is specific and is not a substitute for xenogenic and autogenous bone materials in dentistry. Biodegradable bone graft substitute is used in cases of orthopedic trauma, spine and cranio-maxillofacial surgeries to fill bone voids and gaps that are not characterized by the strength of the bone structure, and the substitute is not designed to withstand bearing loads without traditional rigid fixation.
Use of biodegradable implants in facial and maxillofacial surgery
In maxillofacial surgery, biodegradable implants are used for the following purposes:
-
-
- Bone replacement. Biodegradable implants can be used to restore bone tissue that has been damaged by injury, disease, or surgery.
- Bone graft attachment. Biodegradable implants can be used to anchor bone grafts that are used to repair lost or damaged tissue.
- Soft Tissue Support. Biodegradable implants can be used to support soft tissue, such as cheeks or lips.
-
Use of biodegradable implants in dentistry
In dentistry, biodegradable implants are used for the following purposes:
-
-
- Temporary support for metal implants until the patient’s own bone tissue regenerates. Can also be used to support reimplanted teeth after accidents or other injuries.
- Stimulation of bone growth. Biodegradable membranes and meshes can be used in directed bone regeneration surgeries to stimulate bone growth, such as in cases of jawbone atrophy.
-
Examples of clinical applications of biodegradable implants
-
-
- Bone replacement. A patient with a jaw fracture was operated on using biodegradable implants to replace the damaged bone tissue. The implants were gradually resorbed in the body while the damaged bone tissue regenerated.
- Bone graft attachment. A patient with bone deficiency underwent bone grafting surgery. Biodegradable implants were used to anchor the bone graft, which provided support and fixation of the graft.
-
Materials used to make biodegradable implants
In the early days of implants, animal tissues and metals were used, but today neutral materials that do not cause rejection or allergic reactions are used.
Polymers. Polymers are synthetic materials that can be resorbed in the body. They are used to make biodegradable implants in a variety of shapes and sizes.
- Polymers. Meaning biodegradable implants based on:- Lactic acid (L-lactide: Very strong, long to disintegrate);
– Glycolic acid (glycolide: Very rapidly resorbed);
– L,D-lactide: Plastic, forms a rapidly disintegrating crystal lattice;
– trimethylene carbonate (TMC: Plastic).These components are natural to the human body. The optimal ratio of these polymers is selected for each implant, depending on the properties that the final product should have (strength, elasticity, plasticity, degradation time). Due to their composition, biodegradable implants degrade over time by hydrolysis into alpha-hydroxyl acids and are metabolized by the body.
- Metals. Biodegradable metals include:- Magnesium-based alloys;
– iron-based alloys;
– Zinc compounds have recently been studied in this regard.
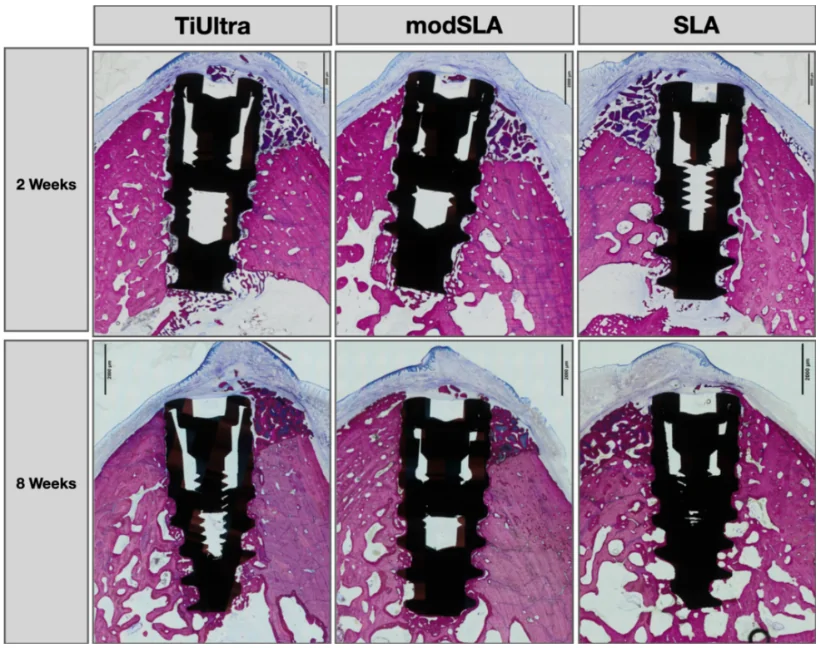
Also used are metal implants made of titanium with biodegradable coatings based on hydroxyapatite, calcium phosphate vitreous ionomers, which promote bone growth and are metabolized by the body over time. Biodegradable coatings can accelerate the process of osseointegration.
In the future, biodegradable materials will be increasingly used for complex dental cases and hybrid components that contain a degradable and a permanent part will be used more frequently than at present.